A Tutorial Series CSS for Beginners: Border, Outline, Margins, Padding & More!
Recap of Last Tutorial
In my last tutorial and the first in this series entitled, "A Tutorial Series CSS for Beginners: Formatting Text, Links & Lists'" we looked extensively at color, text alignment of paragraphs, text decoration: underline, overline, and "strike through"; text transformation (e.g. all characters to uppercase, the formatting of links (e.g.) when hovering, and list formatting. We did not get to fonts which we will cover briefly next. Most of what was in the least tutorial was basic and straightforward. It more or less amounts to being familiar with what options are available and which work for you in your implementation.
Focus for this Tutorial: Outline, Margin, Border, and Padding
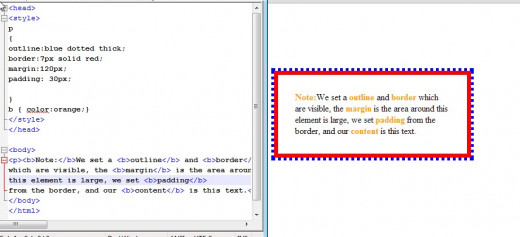
The properties of outline, margin, border, and padding along with the HTML element content are referred to as a box. In fact all HTML elements can be considered boxes. So what we are looking at with the various CSS properties in this tutorial is referred to as the CSS box model.Property values for outline, margin, border, and padding (along with content) determine the space requirement for the element, Placement of elements is important in making the page attractive and noteworthy. Thus, making corr
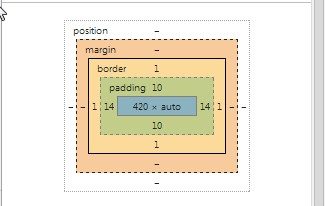
In fact, it is so fundamental that when display a page with the “inspect element” to step through the actual code of a page. an illustration of the box at that point in the page is presented, as the snapshot illustrates.
ect assesment as to whether the elements will "fit" is essential.
A HTML Element Box from an "Inspect Element"
The Five Components of Element Size
The five components which contribute to element size are:
- Margin- An area around the outline which is devoid of a background color. The margin is transparent
- Outline - An outline is a line that is drawn outside the border to enhance the border. The outline properties specify the style, color, and width of an outline.
-
Border - A border surrounds the padding and content. The border color is inherited from the color property of the box.
-
Padding -Clears an area around the content. The padding is affected by the background color of the box.
- Content -The text and image area.
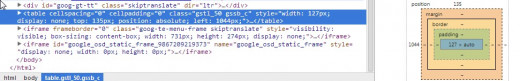
The snapshot illustrates an example where all five elements are specified.
An Example of Margin, Outline, Border, Padding, & Content
Calculating the Space Requirements for an Element
There is only so much space, so much “real estate” on a page. It becomes important to know how you want a page to look taking into account the total size of the elements. For example you have two elements A and B which you would like to have sit horizontally together side by side. If the width of the two combined exceeds the page width, the second element will be shifted down.
A Space Calculation Example
Suppose the element had the following properties:
width: 200px;
height 200px;
padding: 10 px;
margin: 10px;
border: 5px solid green;
The computation for the total area would be
width = height since our parameters for padding, margin, and border are equal on all sides. (This need not be the case, different values can be specified for each of the four sides (top, bottom, left, and right).
width = {width of element} + 2 X (width of padding, left and right) + 2 X (margin) + 2 X (border)
therefore, we arrive at a width (and height) of 250px. The element size is 250px by 250 px.
Our calculation is was a little bit less involved than the general calculation where borders, padding, and margins, and outline might not been identical. In general one would have:
Total element width = width + left padding + right padding + left border + right border + left margin + right margin + left outline + right outline
and
Total element height = height + top padding + bottom padding + top border + bottom border + top margin + bottom margin + left outline + right outline
Borders Come in Many "Flavors"
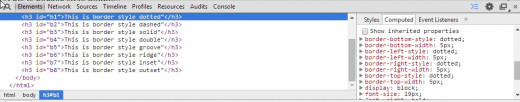
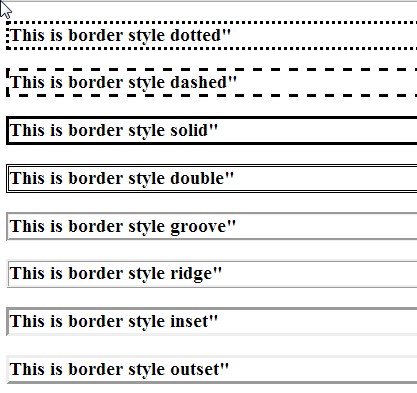
There are 8 types of borders currently defined. The are used by specifying the border-style value. The styles are named: dashed, dotted, double, solid, inset, outset, grooved, ridge.
Border-styles :
- Border width is specified in pixels or to a value of thick, thin, or medium.
- Border color. can also be set to transparent.
- border-style-top, -right, -left, - bottom The values can be specified individually as such border-style-top, border-style-right, eyc. However there is a short cut method. One specify border-style with up to four values.
Depending on how many values are specified. The way the values are determined for top, bottom, left, and right are as follows:
border-style: value1 value2 value3 value4
- top border is value1
- right border is value2
- bottom border is value3
- left border is value4
border-style: value1 value2 value3;
-
top border is value1
-
right and left borders are value2
- bottom border is value3
border-style: value1 value2;
- top and bottom borders are value1
- right and left borders are value2
border-style: value1;
- all four borders are value1.
If you have a uniform border (all side the same) then you can specify border simply as
border: <width> <style> <color> ; on one line. Example:
border: 8px solid blue;
Border Styles
Outline
Outline
An outline is a line that is drawn outside the borders to make the element "stand out".The outline properties specify the color, style, and width.
As with border there is a shorthand way to describe outline properties
outline <color>, style, width
where:
width – thin, medium, thick, px
style – same 8 as border
color – rgb, hex, name invert (Yes. colors can be inverted.)
Padding
The padding clears an area around the content of an element. The padding is affected by the background color of the element.
As with top, right, bottom, and left padding can be changed independently using separate properties: padding-top, padding-right, etc. . A shorthand padding property can also be used, to change all paddings at once. Padding can be specified as a size as in the example which follows or as a percentage of the "container" element., the outlined or bordered area
padding-top:25px;
padding-bottom:25px;
padding-right:50px;
padding-left:50px;
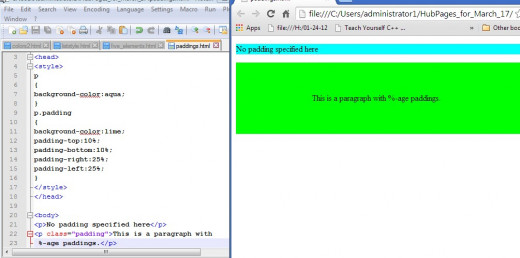
The snapshot illustrates a padding example given in percentages.
Padding Examples: No Specific Padding and Padding as %-age
CSS Font Properties
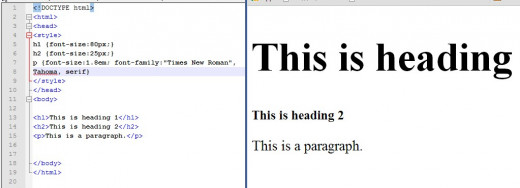
There are four items to remember about fonts. There are font families such as Times New Roman, Tahoma, Arial which are popular. There are also generic fonts which are named monospace or serif.
When targeting a specific element such as a paragraph. It is a good idea to specify more than one font. In this way, if the preferred font is not available, the "fallback" font can be used. Beside the choice of font one can specify a font-style of normal, italic, or oblique (almost like italic, but used less frequently. Font size is nowadays mainly stated in terms of px (with dx, density pixels being common for mobile) but one can use em, which is a measure equal to the current font size. Thus 2em, for example is twice font size. We will discuss "em" further when we look at various units of measurement in CSS.
Illustrating Some Font Properties
Wrap Up and What's Next
In this tutorial we covered the five components which make up the area that is reserved form a HTML element. HTML elements are considered CSS boxes when the are formatted. These calculations are vital when one starts to layout a web page as we will see in the near future. We briefly touched on the subject of fonts. Choosing"safe" fonts which are likely to be present on all machines is a good practice. I am currently working on a hub which addresses typographic elements is some detail.
In the next tutorial, now that we have the concept of HTML boxes and how to size them, we will start looking at aspect of page layout.